
UL measures the temperature rise of a fuse-holder using a solid copper dummy fuse. This means that only fuses of this type with a rated current of 1 A maximum can be used in combination with the fuse-holder under consideration. 1 A show a maximum power dissipation of 2.5 W or less. Fuse links of this type with rated currents of max. High breaking capacity fuses specified in IEC 127, part 2 standard sheet I, however, show power dissipations up to 4 W at highest ratings (see table 4.3). For these fuse types the fuse-holder under consideration is able to accept all fuse ratings up till 6.3 A of this type of fuse links. Quick-acting fuse links specified in IEC 127 part 2, standard sheet II, have power dissipations which do not exceed 2.5 W (see table 4.3). As an example, let us assume that the rated accepted power of a fuse-holder is 2.5 W.
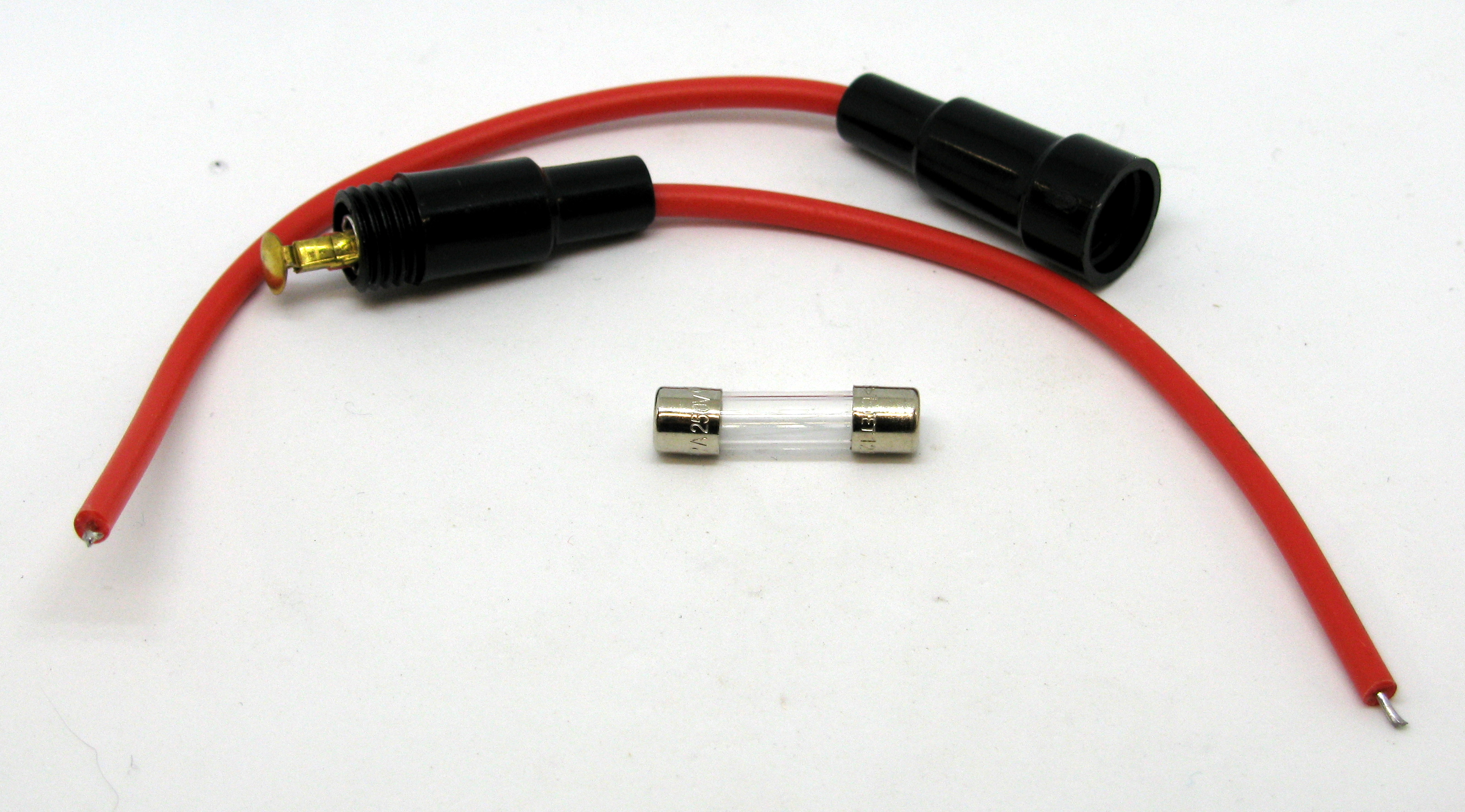
Basically, this means that the rated current is not a fixed value. This rated accepted power determines the rated current. For example, it means that at a power dissipation of 4 W (by a fuse link placed in the fuseholder) temperatures of the fuse-holder should not exceed certain limit values as specified in the standard. The rated accepted power is, according to IEC 257, "A stated value of power dissipation (of a fuse link) which a fuse-base or fuse-holder can accept under prescribed conditions of use and behavior." Rated values of accepted power are 1.6 W, 2.5 W or 4 W.

According to IEC 257, the rated current is determined by the rated accepted power of a fuse-holder. Considerable differences exist between the IEC and the UL standards regarding the rated current of a fuse-holder. In the following, some of the most important differences between the two standards will be indicated.įrom an application point of view, a fuse-holder is characterized by the features discussed in the previous section by its rated values for voltage, current, and accepted power. In the case of fuse links, compliance with the UL-standard does not usually mean that the fuse-holder under consideration meets IEC-requirements and vice versa. 2 to this publication dated January 1989.īoth standards show considerable differences. IEC-publication 257 (1968) and Amendment no.The most important standards for fuse-holders, which specify requirements, characteristics and testing methods are: How much is available to spend on safety and reliability?.Should the fuse only be accessible from outside the appliance?.Should the end customer of the appliance have access to change the fuse?.How often will the fuse need to be replaced?.Will the fuse need to accessible for replacement?.The first step is to answer the following questions: Selection of the Fuse and Holder Solution


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
